Tracheal glands are prominent in the submucosa. The hyphae of rhizopus species are typically non-septate fast-growers and white in colour.
Tissue Type Best Provide At Least 2 Unique Chegg Com
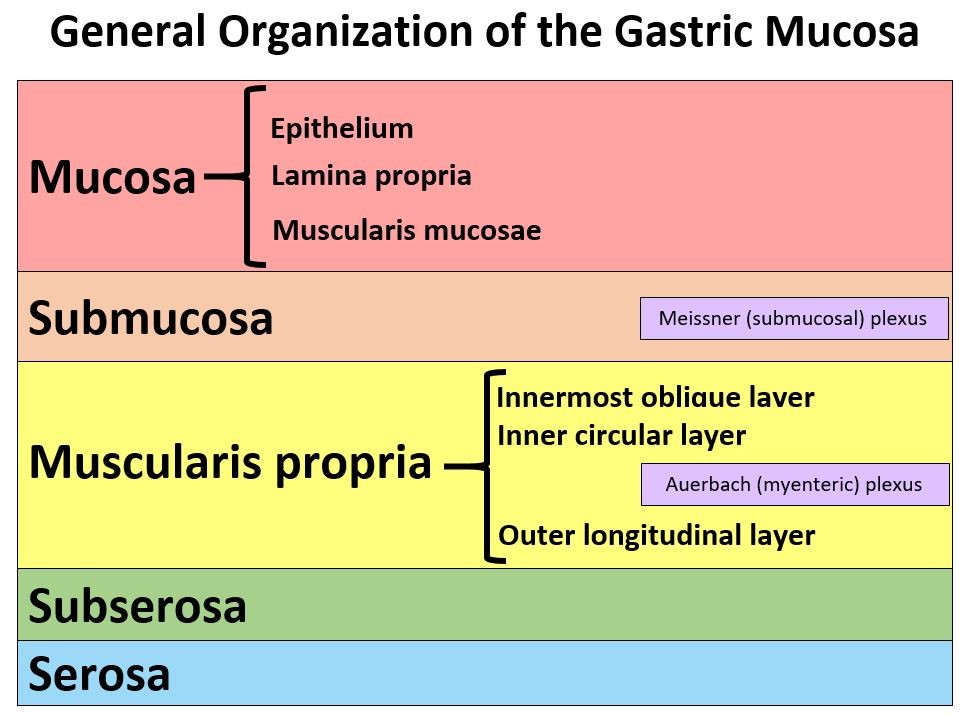
The epithelium of the mucosa is pseudostratificed columnar epithelium with cilia.
2 unique identifying features of mucosa. The epithelium is tall columnar pseudostratified with cilia and goblet cells. It secretes mucus enzymes and hormone. The respiratory mucosa is made up of the epithelium and supporting lamina propria.
The submucosa composed of areolar connective tissue surrounds the mucosa and contains blood and lymph vessels as well as nerves that serve nearby tissues. Its arrangement means that it is durable yet flexible and mobile. Sect HE View Virtual Slide Slide 125-3 larynx sag.
The mucosa is highly folded. B type II pneumocytes. In this context we will discuss the features structure and the different reproduction methods in Rhizopus.
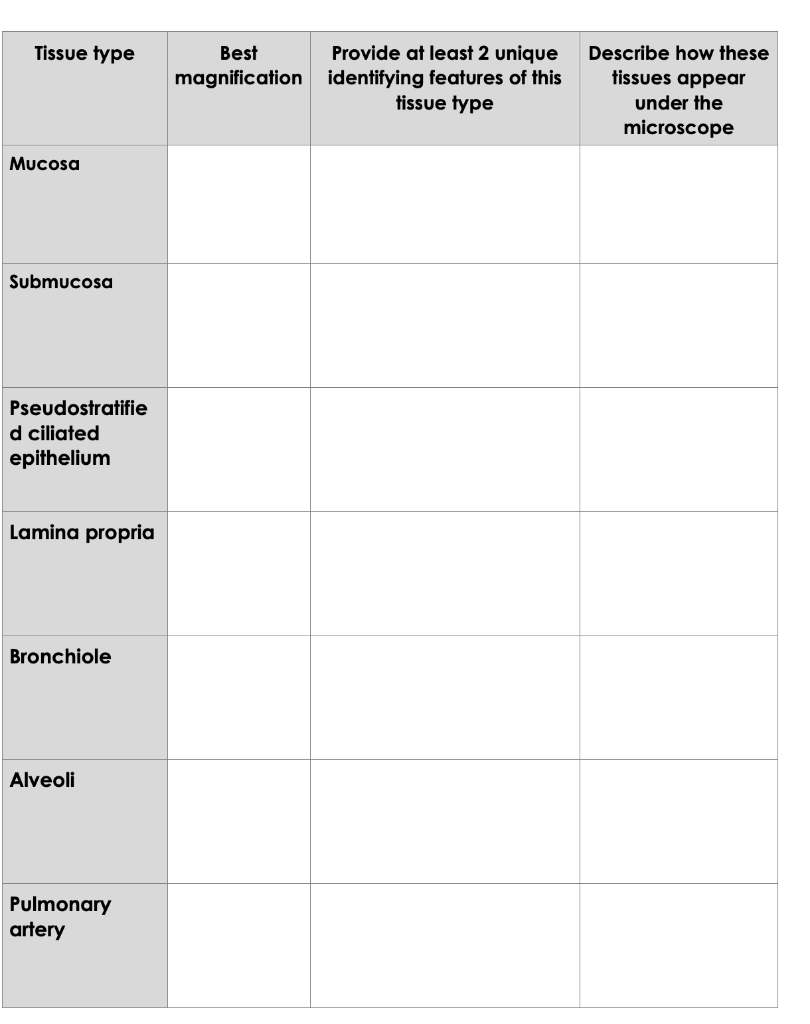
The hyaline cartilage is very prominent. The mucosa is roughly separated from the submucosa by a layer of longitudinal elastic fibers --the trachea in this sample is cut in cross section so the elastic fibers will also be in cross section and can be seen here as eosinophilic glass-like dots example. 3 Data table Tissue type Best magnificati on Provide at least 2 unique identifying features of this tissue type Describe how these tissues appear under the microscope Mucosa 100x Lamina propria and the Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelia It has a dark purple appearance with a presence of epithelial Submucosa 100x The tracheal gland and the Fibrous connective tissue It is a light purple and seems.
The mucosa as always consists of epithelium and underlying connective tissue In the upper left quadrant of the field is a large branch of the pulmonary artery with it s bright pink tunica media smooth muscle coat. The muscularis mucosae is also thick and in some areas it consists of 3 layers of smooth muscle although this layering is. Large circular folds called plicae circulares shown in the diagram to the right most numerous in the upper part of the small intestine.
The width of the vessels are seldom more than quarter the width of the non- vascular area of the mucosal unit. The bronchial mucosa also contains a small cluster of neuroendocrine cells also known as Kulchitsky cells. A type I pneumocytes squamous epithelial cells - simple squamous epithelium cells connected by desmosomes.
Aside from rich vasculature and lymphatics this layer also holds the submucosal Meissners plexus. - very thin cytoplasm only the nuclei can be seen with the LM. The main identifying feature of the Rhizopus species is the presence of rhizoids at the base.
Slide 125-2 larynx sag. A thin layer of bright pink smooth muscle lies between the cartilage and the mucosa. Smaller folds called villi which are finger like mucosal projections about 1mm long.
Sect HE View Virtual Slide The mucosal surface of the rest of the conducting portion is lined by respiratory epithelium except the true vocal fold vocal cord or vocal ligament View Image in the larynx which is lined by a stratified sometimes keratinized. On histology slide it is a little hard at this magnification to actually see the details of the mucosa. This includes catecholamine and polypeptide hormones such as serotonin calcitonin and.
The mucosa of trachea consists of respiratory lining epithelium and lamina propria. The mucosa is relatively thick and contains numerous tubular glands. The mucosa of the large intestine is smooth lacking the villi found in the small intestine.
Many mucous glands secrete mucus into the hollow lumen of the large intestine to lubricate its surface and protect it from rough food particles. The vessels are single or multiple and tend to run a tortuous course. Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium cells these are tall densly packed cell having apical cilia most predominant in domestic mammals 2.
The innermost layer known as the mucosa is made of simple columnar epithelial tissue. They have neurosecretory type granules and can secrete several factors. In the trachea lining epithelium you will find different types of cells 1.
The supporting lamina propria underneath the epithelium contains elastin that plays a role in the elastic recoil of the trachea during inspiration and expiration together with blood vessels that warm the air. 4 Tissue type Best magnificati on Provide at least 2 unique identifying features of this tissue type Describe how these tissues appear under the microscope Mucosa 400x-Includes pseudostratified ciliated epithelium-near the apical side Compact and similar looking cells Submucosa 400x-Fibrous connective tissue -has tracheal glands Dark circles embedded within tissue Pseudostrati fied ciliated epithelium. These mucosal units are most commonly circular or elliptical and occasionally rectangular or hexagonal fig.
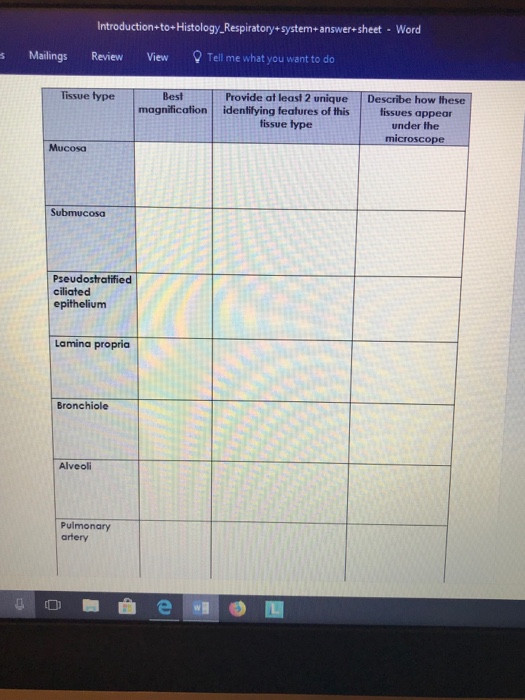
The mucosa is coated with simple columnar epithelium. Tissue type Best Provide at least 2 unique magnification identifying features of this tissue type Describe how these tissues appear under the microscope Mucosa Submucosa Pseudostratifie d ciliated epithelium Lamina propria Bronchiole Alveoli Pulmonary artery. Deep to the mucosa is a thick layer of connective tissue known as the gastric submucosa.
And absorbs digested end-products. The layer under the mucosa is the submucosa wherein youll find numerous seromucous glands. IntroductiontoHistology_Respiratorysystemanswersheet - Word s Mailings Review View Tell me what you want to do Tissue type Best Provide at least 2 unique Describe how these magnification identifying features of this lissues appear tissue type under the microscope Mucosa Submucosa Pseudostratified ciliated epitheliunm Lamina propria Bronchiole Alveoli Pulmonary artery.
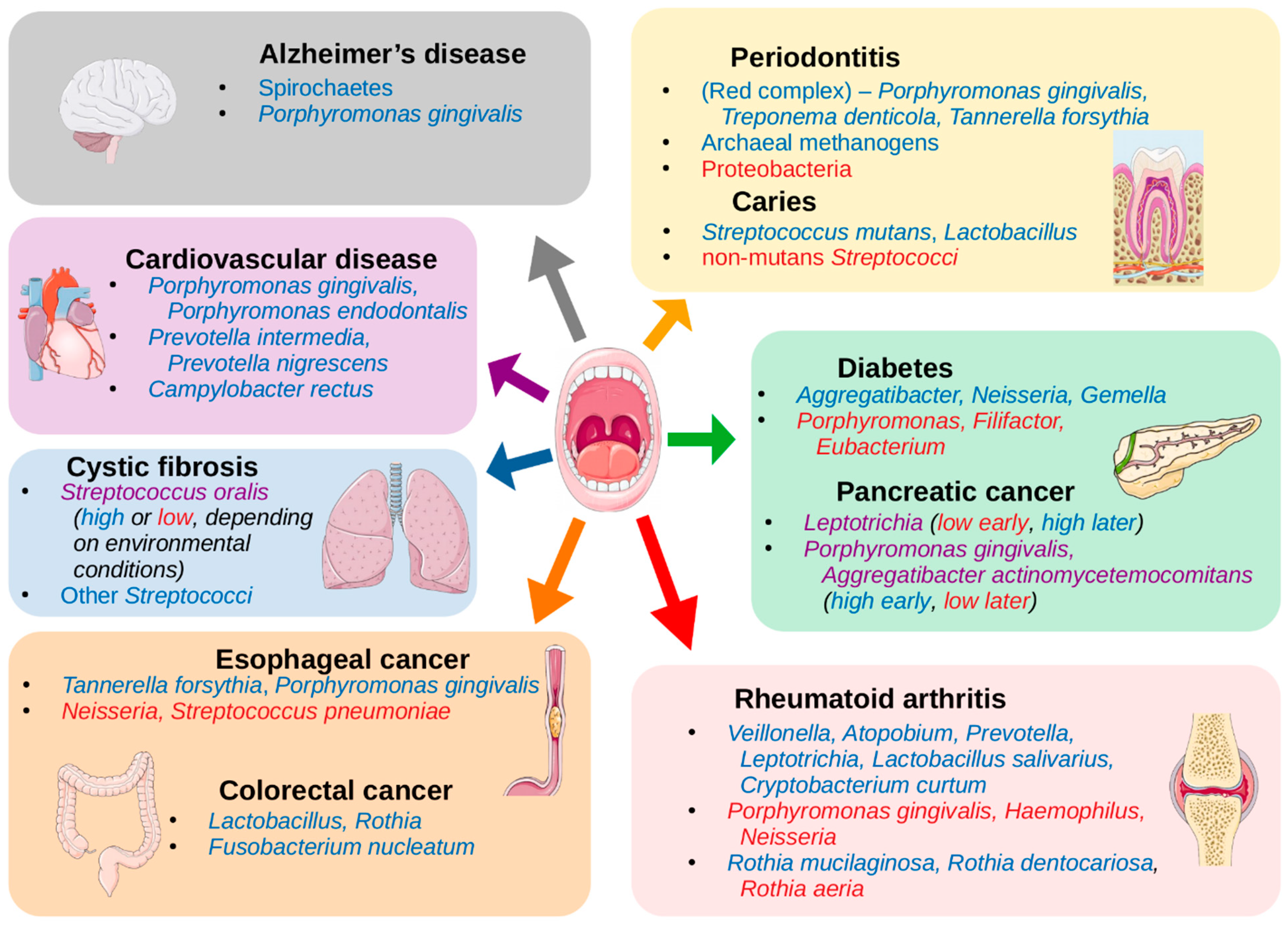
Microorganisms Free Full Text The Human Oral Microbiome In Health And Disease From Sequences To Ecosystems Html
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/12176/stomach-mucosa-and-muscular-layers_english.jpg)
Stomach Histology Mucosa Glands And Layers Kenhub
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/12270/Gastric_wall_-_English.png)
Stomach Histology Mucosa Glands And Layers Kenhub
Anatomy Head And Neck Oral Gingiva Article
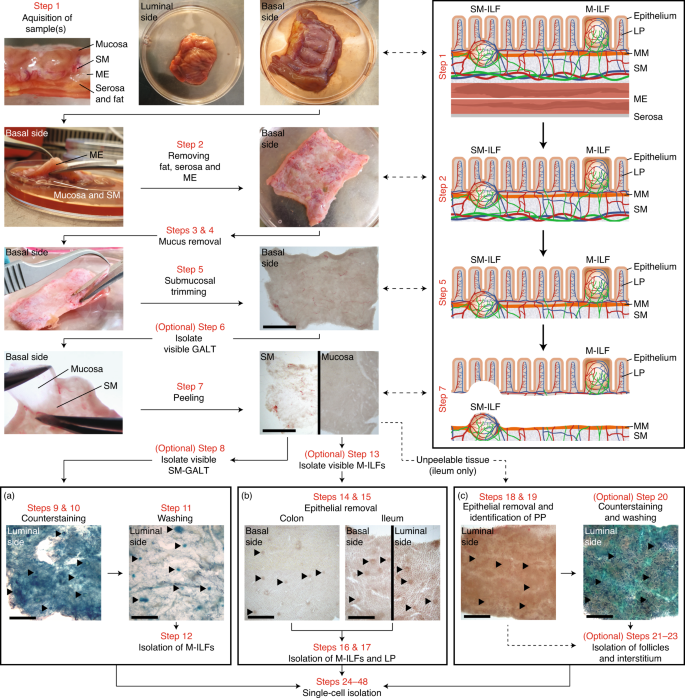
Identification Isolation And Analysis Of Human Gut Associated Lymphoid Tissues Nature Protocols
Female Reproductive System Lab

The Small And Large Intestines Anatomy And Physiology Ii
Provide At Least Two Unique Identifying Features Of Chegg Com
0 comments:
Post a Comment